To
Researchers
- TOP
- To Researchers
Lineup
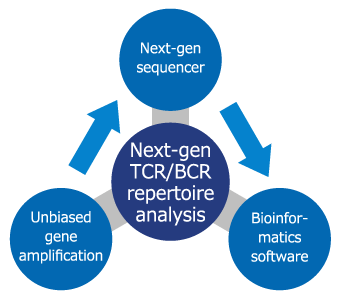
TCR/BCR Repertoire Analysis
Neoepitope Analysis

By conducting RNA seq and Exose seq together, specific gene mutations which are specific to individual cancers can be identified. In addition, by taking into account intermolecular coupling, variant peptides (neoepitope) capable of presenting an antigen will be identified. This identification can also be used for indel, long indel, and splicing variants using sequence data.
16S rRNA Bacterial Flora Analysis

Distribution of bacterial species (bacterial flora) in samples can be analyzed by examining the V1V2 or V3V4 region of the 16S rRNA gene preserved in each bacterial species using next generation sequencing. This analysis can be applied not only to biologically derived samples (feces, saliva, etc.), but also to environmentally derived samples (soil, food, etc.).
Publications
- 2024/10/23
- Paper
-
Clinical immunity
Low-frequency CD8+ T cells induced by SIGN-R1+ macrophage-targeted vaccine confer SARS-CoV-2 clearance in miceA research group led by Dr. Daisuke MURAOKA, Division of Translational Oncoimmunology, Aichi Cancer Center Research Institute, Dr. MOI MENG LING, School of International Health, Graduate School of Medicine, the University of Tokyo, Dr. Kazunari AKIYOSHI, Department of Immunology, Graduate School of Medicine, Kyoto University, Dr. Hiroaki IKEDA, Department of Oncology, Nagasaki University Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences, and Dr. Naozumi Harada, United Immunity, Co., Ltd.,, have demonstrated that the selective delivery of PNG to medullary macrophages depends on its binding to the C-type lectin SIGN-R1.
This induction of specific CD8-positive killer T cells that respond rapidly to viral infection, even at low frequencies, is critical for vaccine efficacy and can be achieved by targeting SIGN-R1+ myeloid macrophages.
In this study, our T-cell receptor (TCR) Repertoire Analysis technology was used as a method to identify clonal differences in induced CD8-positive killer T cells.The results of this research are published in a news release on the following website.
Tokyo University: Research publication on PNG based infectious disease vaccine development
Kyoto University: 我が国独自のナノ粒子性薬剤送達システムを用いた次世代ワクチンの新型コロナウイルスに対する優れたキラーT細胞誘導と感染防御性能を動物モデルで実証―将来の感染症ワクチン開発への幅広い応用の可能性― (Japanese)
Nagasaki University: T細胞誘導と感染防御性能を動物モデルで実証 (Japanese)
Aichi Cancer Center: T細胞誘導と感染防御性能を動物モデルで実証 (Japanese)
United Immunity Co., Ltd.: A Next-Generation COVID-19 Vaccine Using Myeloid Targeting PlatformTM Shows Superior Killer T Cell Induction and Infection Protection Properties in a Preclinical Animal Model
- 2024/09/12
- Paper
-
Cancer Research Communications
Solid tumor
Therapeutic efficacy of IL-7/CCL19-expressing CAR-T cells in intractable solid tumor models of glioblastoma and pancreatic cancerA paper utilizing our TCR Repertoire Analysis was published by Dr. Keisuke Ota, Department of Immunology, Yamaguchi University Graduate School of Medicine, who has investigated the therapeutic efficacy of next-generation CAR-T cells (7×19 CAR-T) that produce IL-7 and CCL19 against glioblastoma and pancreatic cancer, which are refractory cancers, using mouse models.
To confirm the cytotoxic activity and therapeutic efficacy of 7×19 CAR-T, they experimented two models using anti-EGFRvIII CAR-T generated from epidermal growth factor receptor variant III (EGFRvIII)-positive glioblastoma and healthy donor PBMCs, and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-positive pancreatic cancer organoids and in vitro and in vivo evaluation in models with anti-HER2 CAR-Ts generated from PBMCs of the same patients. The results by each experiment were induced the result in prolonged survival in mice. This study is the first to demonstrate the therapeutic efficacy of next-generation CAR-T in an autologous model using patient-derived tumor organoid and CAR-T generated from the same patient's PBMC, in which unwanted allogeneic immune responses are fully excluded.
We have performed a Repertoire Analysis using TCR α and β chains before (from PBMC creation) and after (from splenocytes) injection of 7×19 CAR-Ts sorted CAR-positive and negative T cells.
- 2024/08/15
- Paper
-
Clinical immunity
Analysis of B-cell receptor repertoire to evaluate immunogenicity of monovalent Omicron XBB.1.5 mRNA vaccinesA paper utilizing our Repertoire Analysis was published by Dr. Yohei Funakoshi and Dr. Kimikazu Yakushijin, the Department of Medicine, Division of Medical Oncology/Hematology, Kobe University Hospital and Graduate School of Medicine, and Dr. Goh Ohji, the Department of Microbiology and Infectious Diseases, Division of Infection Disease Therapeutics, Kobe University Hospital.
In this paper, they evaluated the Omicron XBB.1.5 mRNA vaccine using a new novel coronavirus-specific antibody sequence quantification method developed in the laboratory (QASAS method), and the results suggest that antibody production against the Omicron XBB strain is stronger than that of previous vaccines.
Our BCR Repertoire Analysis is used to obtain antibody gene sequences for matching against the novel coronavirus-specific antibody database.
TCR/BCR Repertoire analysis Guidebook
MUST READ! For users considering Repertoire analysis
An easy-to-understand repertoire analysis guidebook has been prepared which explains in plain language for the questions such as what is immune repertoire analysis and what kind of preparation is necessary.
Please request the guidebook from below if desired.